Beyond the Headshot: Using Corporate Video Production to Humanize Your C-Suite
February 11, 2026Key Takeaways
- Understanding the various factors that contribute to hair thinning in women.
- Implementing effective strategies to prevent and manage hair loss.
- Recognizing when to seek professional medical advice for hair concerns.
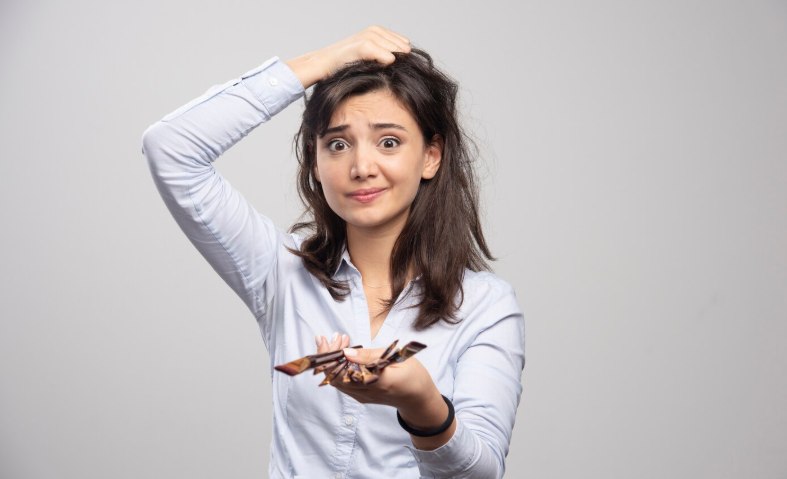
Thinning hair is a widespread concern among women, often affecting confidence and emotional well-being. Everyone loses a small amount of hair daily, and some shedding is a natural part of the hair growth cycle, especially with age. However, when thinning becomes excessive or sudden, it can signal underlying issues or impactful lifestyle factors, and it’s crucial to take action early for the best results. For those looking to support their hair health from within, products designed for women’s unique needs are available at https://nutrafol.com/nutrafol-core-for-women/. Pinpointing the common triggers of hair thinning empowers women to take informed, proactive steps toward fuller hair by tailoring their daily routines and self-care practices.
Hair health is influenced by a complex interplay of genetics, hormones, diet, and daily habits. Unlike many other parts of the body, hair responds noticeably to changes within our internal and external environments, making it an important indicator of overall health. By learning to identify the warning signs and root causes, individuals can better protect their hair and potentially reverse early stages of thinning. Early intervention and lifestyle changes can make a noticeable difference in maintaining a vibrant, healthy appearance. Sometimes, seemingly minor adjustments such as drinking more water, reducing stress, or adding certain foods to your diet can slow or even prevent hair loss progression.
While many women turn to quick cosmetic fixes or temporary solutions, addressing underlying nutrition, stress management, and gentle care can provide lasting results. Focusing on the fundamental aspects of wellness not only supports hair but also contributes to overall health and vitality, making prevention the most effective first step. Regular self-examination and staying vigilant for changes in hair texture, density, or volume can help women become more aware of their hair’s unique needs.
Whether you are experiencing minor shedding or more persistent thinning, implementing holistic strategies and staying informed about hair wellness will help you navigate potential challenges and deliver peace of mind.
Common Causes of Hair Thinning in Women
Hormonal Changes
Changes in hormone levels can significantly influence hair density. Pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid problems all affect the delicate balance responsible for hair growth cycles. During menopause, for example, lower estrogen levels may cause follicles to shrink, resulting in finer, more fragile hair. Hormonal imbalances can also amplify shedding and delay regrowth, making timely management essential. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid imbalances frequently impact hair health, making routine medical screening important for women who notice significant changes in hair texture or density. WebMD discusses how various life stages affect women’s hair health, offering more details on the topic. Managing these hormonal shifts often requires a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, regular exercise, and mindfulness practices.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Proper nutrition is foundational for maintaining strong hair. Inadequate amounts of iron, protein, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients can weaken hair shafts and slow new growth, leaving hair looking dull, brittle, and prone to breakage. Women are particularly vulnerable to iron deficiency, especially during menstruation or after pregnancy, which can accelerate hair loss. Insufficient vitamin B12 and zinc can further diminish hair health, as these nutrients play a critical role in cell reproduction and anchoring hair follicles to the scalp. A protein-deficient diet can also lead to brittle, thinning hair and should be addressed alongside other healthy habits. Including a colorful variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your daily meals helps create an environment that fosters hair regrowth and resilience.
Stress and Psychological Factors
Emotional and physical stress can disrupt the natural growth phases of hair, causing more strands to enter the telogen (resting) phase and shed prematurely, a condition known as telogen effluvium. Prolonged or chronic stress is linked to more pronounced hair thinning, though the good news is that many cases reverse once stress decreases. Incorporating activities such as meditation, regular exercise, and maintaining healthy sleep routines can promote not just hair health but broader physical resilience. Practices like yoga, deep breathing, or journaling can be valuable for stress relief, offering both physical and mental benefits that extend to hair wellness. Being mindful of your mental health and supporting your emotional well-being are among the most significant long-term investments you can make for your hair.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Several common and underlying medical conditions can cause or worsen hair loss. Health conditions such as autoimmune disorders, including alopecia areata and lupus, can result in patchy or diffuse hair loss that often doesn’t resolve with lifestyle changes alone. Furthermore, certain medications like chemotherapy drugs, blood thinners, and some antidepressants may also cause shedding, sometimes creating a cycle that continues until treatment ends. It is vital to consult a healthcare provider if hair loss is sudden, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or skin changes, to identify and properly treat the underlying condition. Having regular checkups and discussing any medication side effects with your provider can help you preserve hair health while managing overall wellness.
Preventive Measures and Treatments
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
Eating a variety of foods rich in vitamins and minerals supplies the scalp and follicles with the nutrients necessary for strong hair, including critical elements like biotin and antioxidant-rich foods. Iron-rich choices such as leafy green vegetables, beans, nuts, and lean meats, as well as vitamin D from sources like salmon and eggs, can significantly improve hair strength and growth. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and flaxseeds, also help maintain scalp health and reduce inflammation that can impact follicles. Keeping hydrated and regulating intake of processed foods helps maintain a supportive environment for hair follicles to thrive, as dehydration or excessive intake of added sugars and unhealthy fats can weaken hair over time.
Gentle Hair Care Practices
Everyday styling choices can impact hair thickness over time, so gentle handling is essential for preservation. Avoiding harsh chemicals and frequent use of hot styling tools will reduce breakage and protect the hair’s natural barrier. Opting for loose hairstyles helps minimize tension on hair follicles, reducing the risk of traction alopecia, a common form of mechanical hair loss linked to tight ponytails, braids, or hair extensions. Using a soft-bristle brush and gentle, sulfate-free shampoos can further protect fragile hair. When detangling, start from the ends and work your way up to avoid unnecessary pulling and breakage. Allowing hair to air-dry when possible and protecting it from sun and wind exposure can also help retain essential moisture.
Medical Treatments
Clinical solutions are available for women facing persistent hair thinning beyond what lifestyle changes alone can address. Topical treatments like minoxidil have proven benefits for many users, stimulating regrowth and slowing shedding. For individuals who need more advanced therapy, options such as prescription medications to correct hormonal imbalances, corticosteroid injections for autoimmune-related hair loss, or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments under a dermatologist’s care may be recommended. These treatments target underlying biological factors and help restore confidence by stimulating the follicles and creating a healthier scalp environment. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the right course of action for your unique situation.
When to Seek Professional Help
If noticeable thinning continues despite home care and dietary improvements, seeking advice from a dermatologist or healthcare professional is critical. Early diagnosis is key to preventing further loss and managing medical conditions that may contribute to hair issues. Medical professionals can perform lab tests, conduct scalp examinations, and take detailed histories to uncover hidden causes and recommend targeted therapies. Persistent, rapid, or patchy loss especially warrants prompt evaluation, as it may signal a treatable health problem. Waiting too long to seek help can limit the effectiveness of certain interventions, so being proactive is essential for the best outcomes.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of the causes and risk factors of hair thinning enables women to stay proactive in prevention and care. By adopting a diet rich in essential nutrients, practicing gentle styling, and seeking medical consultation if necessary, women can safeguard their hair’s health and improve their overall quality of life. Practicing consistent, informed care delivers long-term benefits for hair and well-being, offering peace of mind and supporting self-esteem. When in doubt, seeking reputable, evidence-based advice will ensure you follow the best path to vibrant, beautiful hair at any stage of life.
- Preventing Common Causes of Thinning Hair in Women
- Beyond the Headshot: Using Corporate Video Production to Humanize Your C-Suite
- Making Informed Choices About Cosmetic Dentistry Options
- What To Expect During Your First Visit With a Neurological Surgeon
- How Dermatologists Address Aging Skin Concerns